TOP CATEGORY: Chemicals & Materials | Life Sciences | Banking & Finance | ICT Media

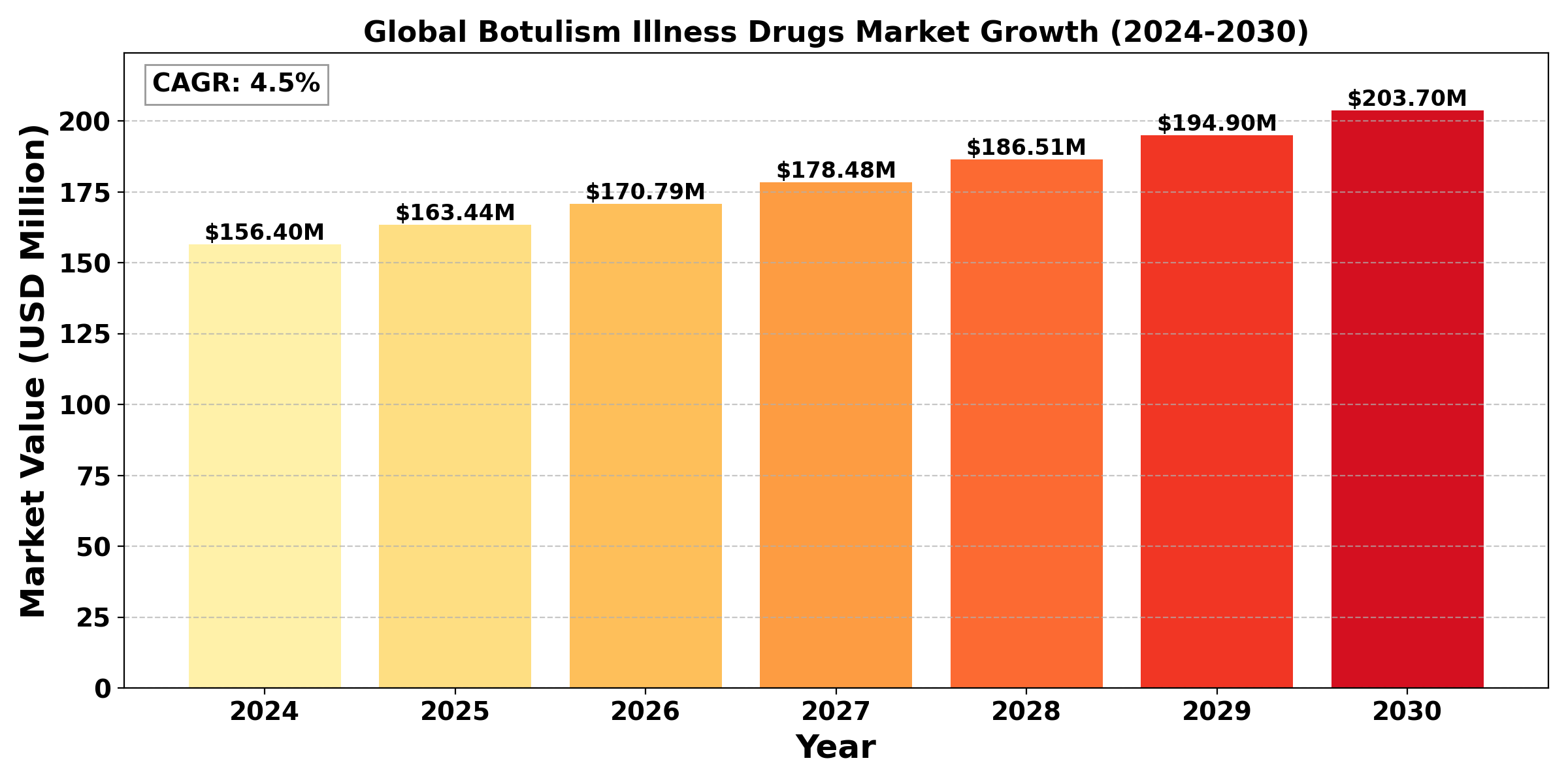
The "Global Botulism Illness Drugs Market" size was valued at US$ 156.4 million in 2024 and is projected to reach US$ 203.7 million by 2030, at a CAGR of 4.5% during the forecast period 2024-2030.
Botulism is a rare and potentially fatal illness caused by a toxin produced by the bacterium Clostridium botulinum. The disease begins with weakness, blurred vision, feeling tired, and trouble speaking. This may then be followed by weakness of the arms, chest muscles, and legs. Vomiting, swelling of the abdomen, and diarrhea may also occur. The disease does not usually affect consciousness or cause a fever.
The goal of the global market for medications to treat botulism is to treat an uncommon but dangerous disease brought on by the bacteria Clostridium botulinum, which generates a strong neurotoxin that can cause paralysis of the muscles and other possibly fatal consequences. Growing awareness of botulism, improvements in diagnostic methods, and the creation of efficient treatments such supportive care therapies and antitoxins are the main factors propelling the market. In order to improve patient outcomes and recovery rates, major firms in the pharmaceutical industry are spending money on research and development to produce new medications and enhance current ones. Regulatory bodies have strengthened food safety procedures in response to the growing prevalence of foodborne botulism, which is frequently linked to inadequately canned or preserved foods. This has indirectly increased demand for botulism medications.
Furthermore, the growing application of botulinum toxin in cosmetic and therapeutic treatments, such as for migraines and spasticity, is expanding the market's scope. Overall, the botulism illness drugs market is evolving, characterized by ongoing innovation and a focus on improving public health outcomes related to this critical health concern.
Segmental Analysis
Antitoxins to hold the highest market share: By Type
Antitoxins have the largest market share in the global market for medications used to treat botulism. Because they neutralize the botulinum toxin before it can injure the patient further, antitoxins are essential for the successful treatment of botulism. In order to lessen the symptoms of the toxin, patients with a diagnosis of botulism are given the most widely used antitoxin, the botulinum antitoxin. The rising knowledge of the disease, along with improvements in healthcare infrastructure and diagnostic tools that enable prompt treatment, are the main causes of this strong demand for antitoxins.
Furthermore, the necessity of quick action in severe botulism cases has highlighted the value of antitoxin treatments, strengthening their place in the market. The need for efficient antitoxin products has increased as a result of the growing prevalence of botulism, especially foodborne botulism connected to inappropriate food preservation techniques.
Hospital to hold the highest market share: By Application
In the global botulism illness drugs market, the hospitals segment holds the largest share among various applications. Hospitals are equipped with the necessary resources and expertise to handle severe cases of botulism, where timely diagnosis and treatment are crucial. The acute nature of botulism, characterized by rapid progression and potentially life-threatening complications, necessitates the availability of specialized care that hospitals can provide. This includes administering antitoxins, supportive therapies, and intensive care for patients experiencing severe neurological symptoms.
The increasing incidence of botulism, combined with heightened awareness among healthcare providers regarding the importance of prompt intervention, drives demand for botulism treatment in hospital settings. Hospitals also benefit from established protocols for managing botulism cases, ensuring that patients receive comprehensive care from specialized medical teams. The clinics segment, while important, typically accounts for a smaller share of the market. Clinics may handle less severe cases or serve as points of initial contact for patients; however, they may lack the
Regional Analysis
The global market for drugs to treat botulism sickness has significant regional variances driven by elements including healthcare systems, the number of botulinum cases, and legal frameworks. Due to a higher number of botulism cases, strong healthcare systems, and growing awareness of food safety, North America—especially the United States—leads the market. The availability of cutting-edge diagnostic equipment and efficient treatment alternatives contributes to the expansion of the industry in this area. Although the total incidence is still lower than in North America, Europe also plays a big part, with nations like Germany and France focusing on food safety laws that reduce the danger of botulism.
Competitive Analysis
A few major companies that concentrate on creating superior antitoxins and supportive care products define the competitive environment of the global market for medications to treat botulism illnesses. The discovery and marketing of botulinum antitoxin treatments, the main therapeutic option for botulism, has allowed leading businesses, like Emergent BioSolutions, to build a strong presence. These businesses frequently profit from exclusive agreements and partnerships with governmental and public health organizations, which give them a consistent demand for public health preparation initiatives and emergency supplies.
End User Analysis
In the global market for medications to treat botulism, hospitals, clinics, and government health organizations are the main end users. Due to their ability to manage serious botulism cases that need prompt medical attention, such as the administration of antitoxins and intensive care for severe neurological symptoms, hospitals make up the largest segment. Hospitals have a crucial role in providing comprehensive care, including monitoring and supporting respiratory functions in advanced cases, due to the severe nature of botulism.
By acting as the initial point of contact for patients exhibiting early symptoms of botulism, clinics also contribute to the market. Clinics are crucial in identifying patients and sending them to specialized facilities, even though they do not have the means to offer comprehensive care.
Government health agencies and emergency preparedness centers are notable end users as they maintain strategic stockpiles of botulism antitoxins. Collaborating with pharmaceutical companies, these agencies ensure rapid availability of treatment for potential outbreaks, enhancing public health resilience. This multi-tiered end-user base underscores the necessity for accessible and effective botulism treatments across various healthcare settings, ensuring timely care for patients and strengthening preparedness against potential botulism risks.
Industry Dynamic
Growing awareness of food safety and toxin-related illnesses
The rising prevalence of foodborne and wound botulism, rising awareness of food safety and toxin-related disorders, and developments in diagnostic and treatment technology are major industry drivers in the global market for medications to treat botulinum infections.
The risk of foodborne botulism has increased as dietary preferences change around the world and processed or preserved foods become more widely available, especially in areas with different regulations for handling and storing food. Healthcare professionals and regulatory bodies are concentrating on early intervention and treatment accessibility as a result of the increased demand for antitoxins and botulism-specific therapies. Furthermore, the need for efficient botulism treatments has increased due to the growth of wound botulism cases, especially those associated with injectable medication usage.
Another important factor is the development of pharmaceutical therapies and diagnostic technologies. Given the illness's swift course, improved diagnostic methods enable faster diagnosis of botulism cases. Botulism medications are becoming more widely available and efficient as a result of pharmaceutical firms funding research to improve antitoxin efficacy and lessen negative effects. These elements, along with government programs encouraging emergency supplies, are driving the market expansion for medications to treat botulism.
Industry Trend
The requirement for early detection and management in cases of botulism has led to a notable trend in the global market for medications to treat the illness: the development of quick diagnostic techniques. In order to enhance patient outcomes, botulism, an uncommon but severe paralytic sickness, needs to be diagnosed quickly and accurately. Delays in treatment can result in serious complications or even death.
Newer diagnostic technologies, including polymerase chain reaction (PCR)-based assays and enzyme-linked immunosorbent assays (ELISA), are gaining traction for their ability to detect botulinum toxin more quickly and precisely than traditional methods. PCR-based assays, for example, target specific genetic markers associated with the bacteria, offering high sensitivity and a relatively quick turnaround, which is essential in clinical and emergency settings. Similarly, ELISA tests, known for their accuracy in detecting proteins or toxins, provide healthcare providers with reliable results in less time
Industry Restraint
Limited Awareness
The market for medications to treat botulism is constrained by a lack of knowledge about the disease. Owing to the condition's rarity, many individuals are not aware of its grave consequences, which include paralysis and death if treatment is not received, or its symptoms, which include breathing problems, swallowing difficulties, and muscle weakness. Because early action is essential to the effectiveness of botulism treatment, this lack of knowledge frequently leads to delayed diagnosis and treatment, which is critical for improving outcomes.
Additionally, the lack of knowledge about botulism among the general public lowers the demand for antitoxin therapies and other forms of treatment. Healthcare professionals in non-specialized settings may fail to recognize botulism symptoms in differential diagnosis, and people may not notice symptoms soon enough to seek prompt medical assistance. In order to raise awareness, enhance early diagnosis, and eventually increase the demand for accessible therapies, public health education on the signs, symptoms, and preventive measures of botulism is crucial.
Public health organizations and regulatory bodies that understand the value of prompt reaction capabilities for possible epidemics or bioterrorism incidents encourage this emphasis on rapid diagnostics. By detecting botulism more quickly and accurately, these sophisticated diagnostic techniques allow for more prompt intervention, improving treatment regimens and boosting public health readiness for this serious disease.
Report Scope
The report includes Global & Regional market status and outlook for 2017-2028. Further, the report provides breakdown details about each region & countries covered in the report. Identifying its sales, sales volume & revenue forecast. With detailed analysis by Type, Application. The report also covers the key players of the industry including Company Profile, Product Specifications, Production Capacity/Sales, Revenue, Price, and Gross Margin 2017-2028 & Sales with a thorough analysis of the market’s competitive landscape and detailed information on vendors and comprehensive details of factors that will challenge the growth of major market vendors.
|
Attributes |
Details |
|
Segments |
By Type
By Application
|
|
Region Covered |
|
|
Key Market Players |
|
|
Report Coverage |
|
Frequently Asked Questions ?
